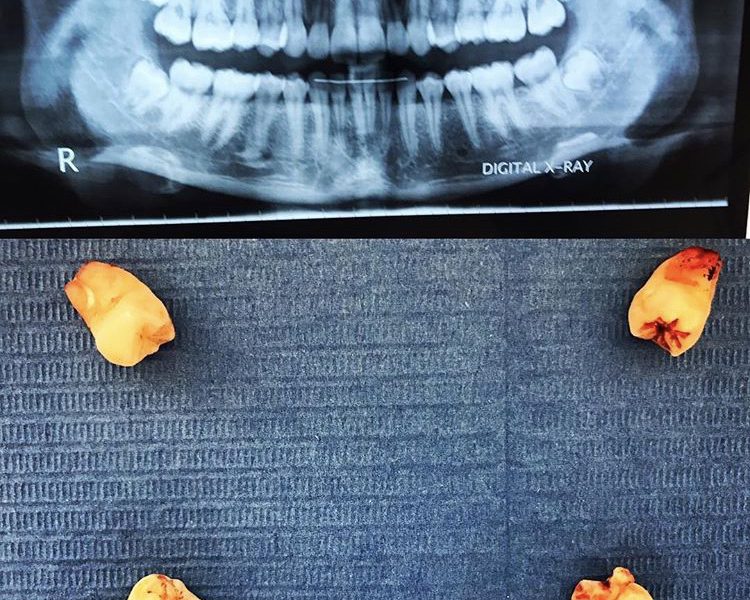
ORAL SURGERY
Wisdom teeth are the most posterior teeth of the jaw. These teeth are the last to erupt in the mouth and this usually occurs between 17 to 30 years of age. Often times wisdom teeth remain impacted or semi-impacted inside the jaw bone due to lack of space for them to erupt. Even when adequate space is present sometimes their direction of eruption or their final position in the jaw is such that they offer no contribution to mastication. On the contrary, they may be the cause of pain or local irritation to the gums due to food impaction since access for proper oral hygiene in the area is typically problematic.
Their extraction is deemed necessary when their presence is accompanied by a series of signs and symptoms such as:
- reduced mouth opening (trismus)
- pain and swelling on the gums surrounding the wisdom tooth (pericoronitis)
- bone loss on the second molar adjacent to the wisdom tooth
- caries (cavity) or resorption of the root of the adjacent second molar
- orthodontic problems
- cyst